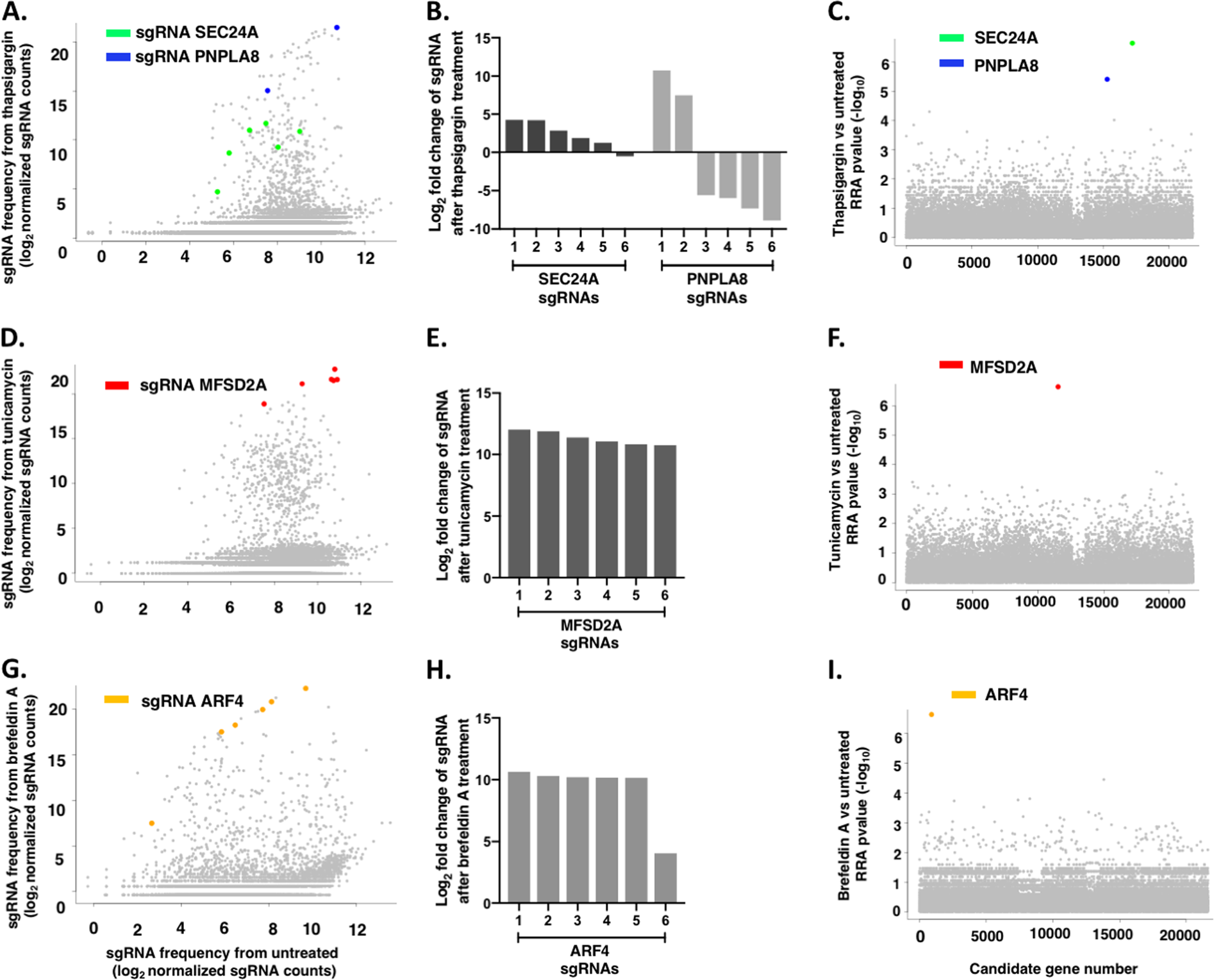
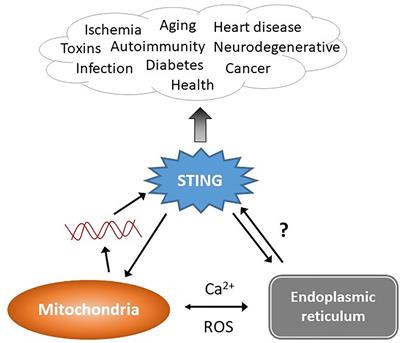
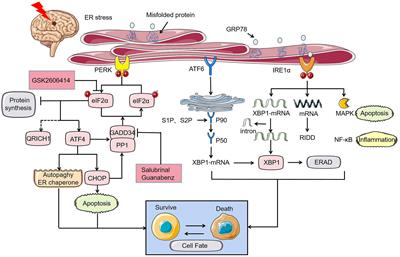
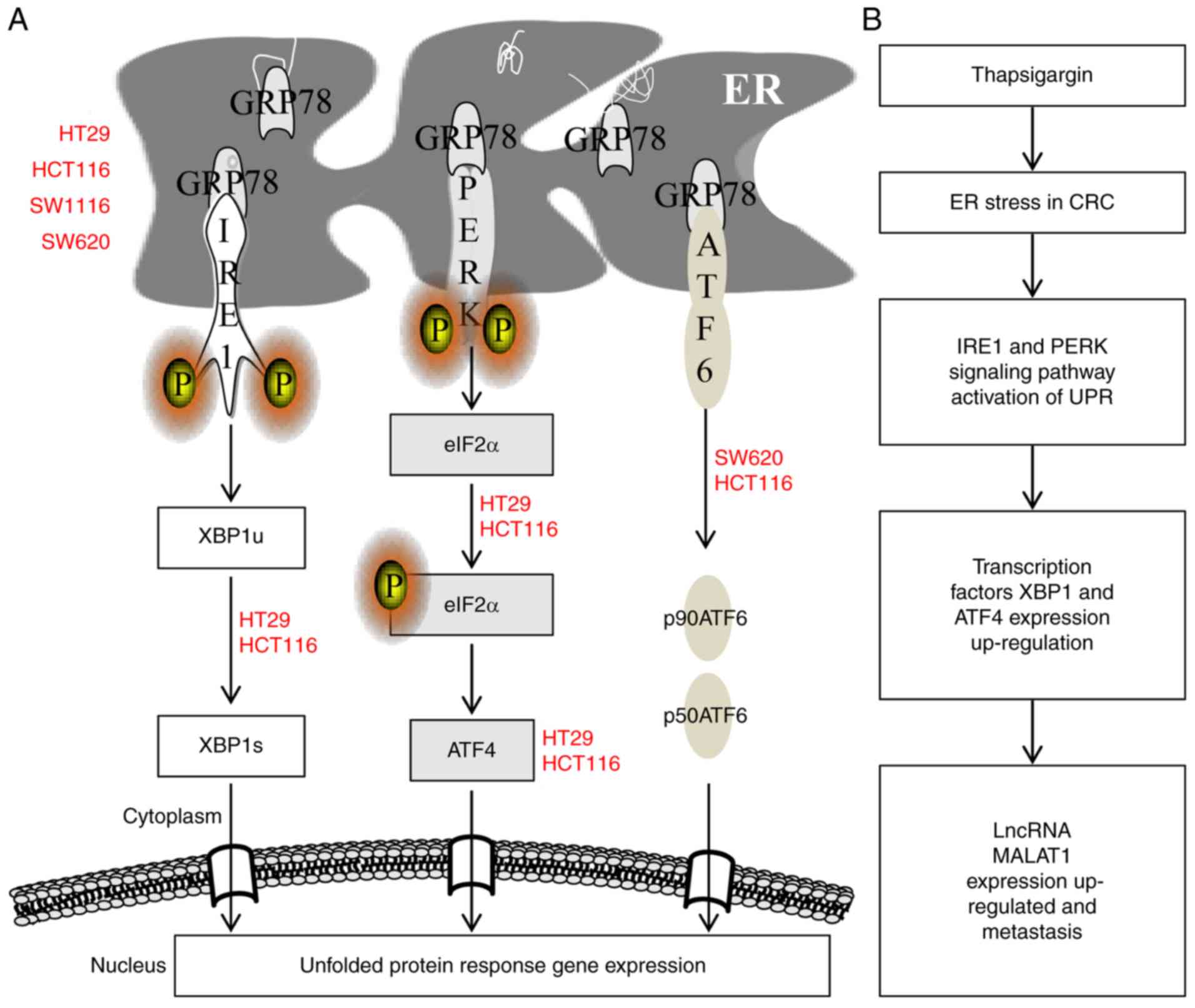
Promising therapeutic effect of thapsigargin nanoparticles on chronic kidney disease through the activation of Nrf2 and FoxO1 | Aging

Cells | Free Full-Text | Calcium Pathways in Human Neutrophils—The Extended Effects of Thapsigargin and ML-9
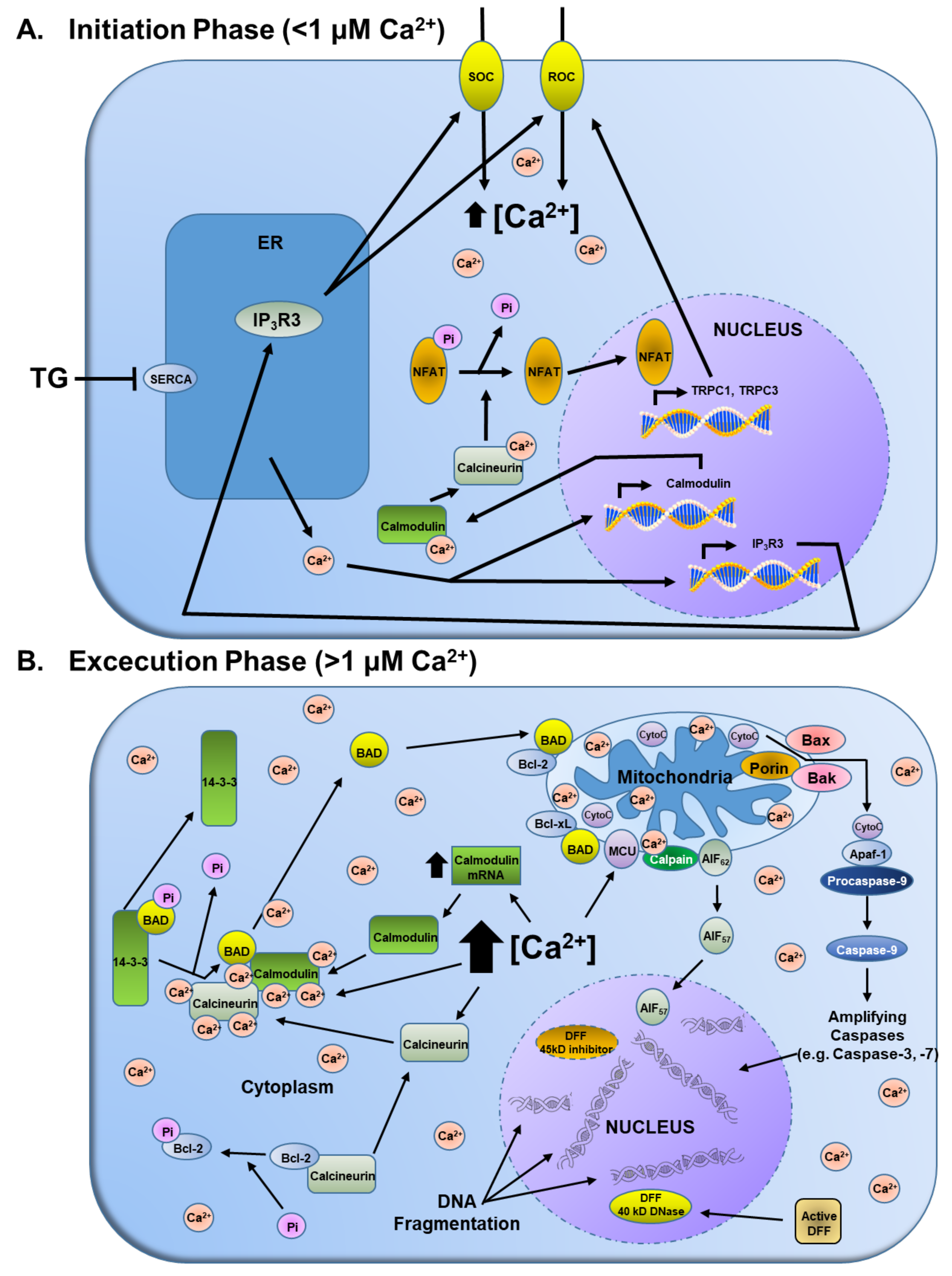
Molecules | Free Full-Text | Mipsagargin: The Beginning—Not the End—of Thapsigargin Prodrug-Based Cancer Therapeutics
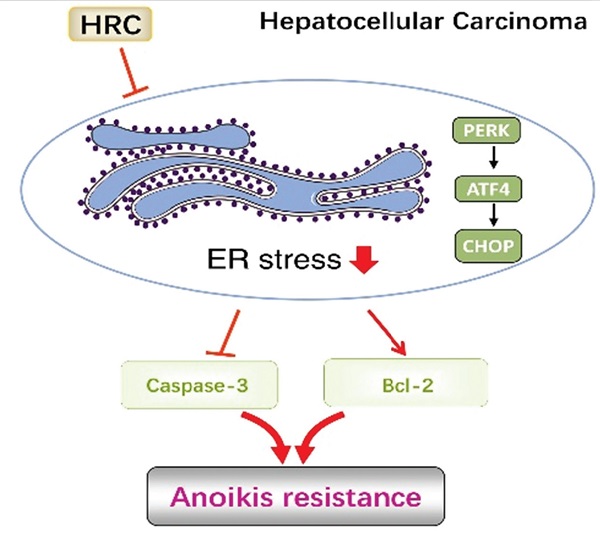
HRC promotes anoikis resistance and metastasis by suppressing endoplasmic reticulum stress in hepatocellular carcinoma

Silybin regulates P450s activity by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress in mouse nonalcoholic fatty liver disease | Acta Pharmacologica Sinica
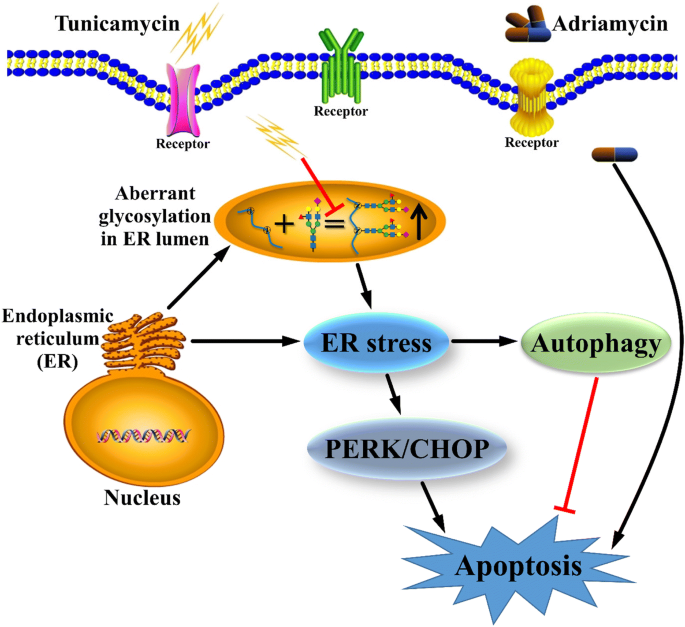
Tunicamycin specifically aggravates ER stress and overcomes chemoresistance in multidrug-resistant gastric cancer cells by inhibiting N-glycosylation | Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research | Full Text

Calcium Influx Caused by ER Stress Inducers Enhances Oncolytic Adenovirus Enadenotucirev Replication and Killing through PKCα Activation: Molecular Therapy - Oncolytics

Luteolin prevents liver from tunicamycin-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress via nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2-dependent sestrin 2 induction - ScienceDirect

Molecular mechanism of ER stress‐induced gene expression of tumor necrosis factor‐related apoptosis‐inducing ligand (TRAIL) in macrophages - Huang - 2015 - The FEBS Journal - Wiley Online Library

Differential impact of imipramine on thapsigargin- and tunicamycin-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells - ScienceDirect

Thapsigargin induces apoptosis when autophagy is inhibited in HepG2 cells and both processes are regulated by ROS-dependent pathway - ScienceDirect
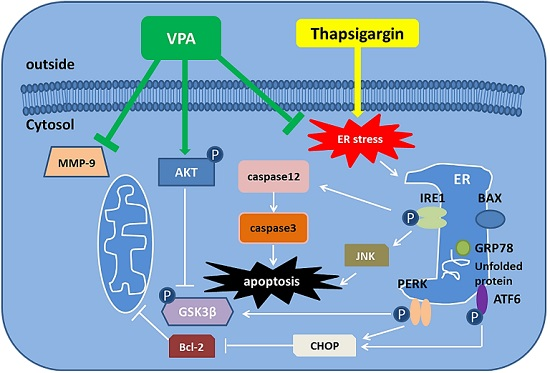
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Valproate Attenuates Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Induced Apoptosis in SH-SY5Y Cells via the AKT/GSK3β Signaling Pathway
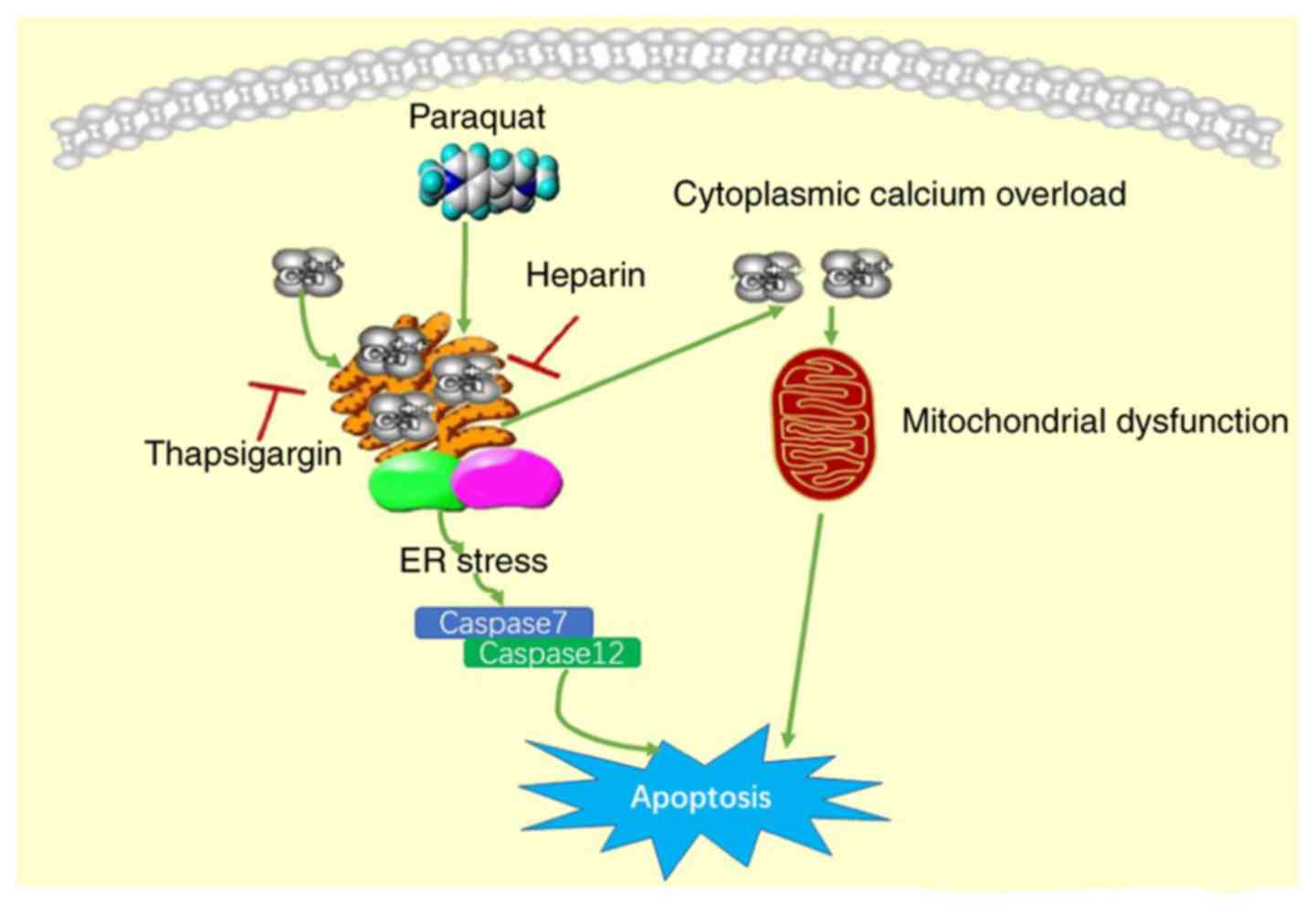
Effect of endoplasmic reticulum calcium on paraquat‑induced apoptosis of human lung type II alveolar epithelial A549 cells
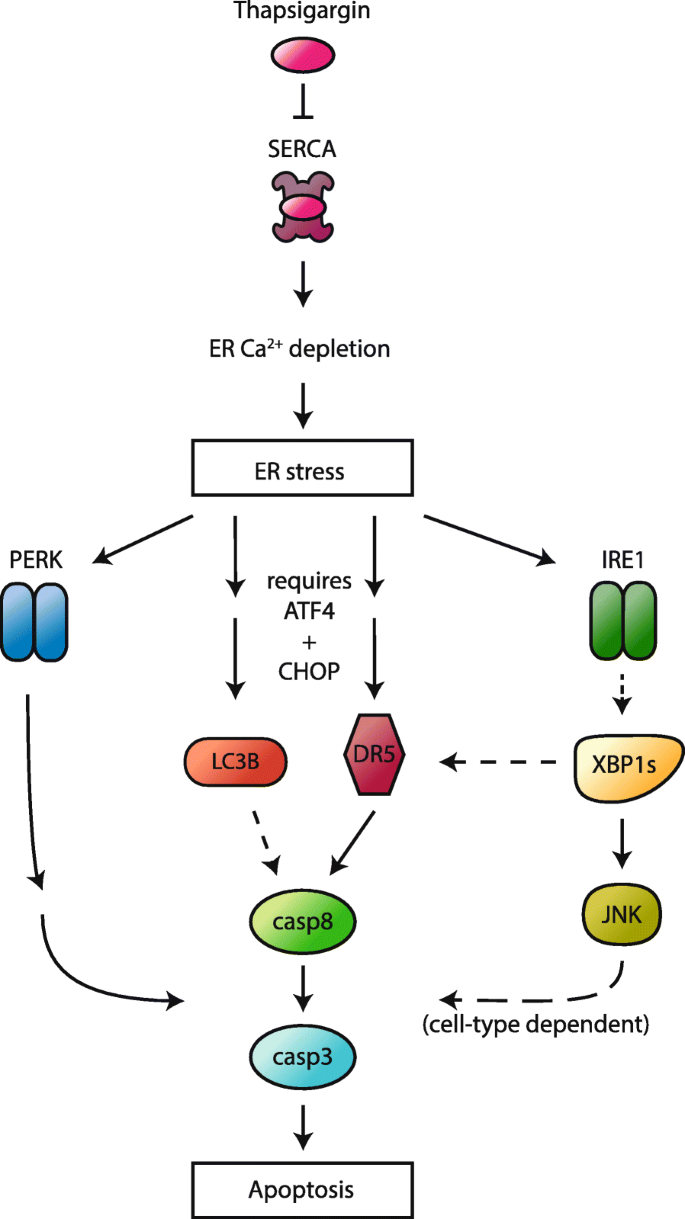
Cell death induced by the ER stressor thapsigargin involves death receptor 5, a non-autophagic function of MAP1LC3B, and distinct contributions from unfolded protein response components | Cell Communication and Signaling | Full Text

Kinetics of Thapsigargin- Ca2+-ATPase (Sarcoplasmic Reticulum) Interaction Reveals a Two-step Binding Mechanism and Picomolar Inhibition * - Journal of Biological Chemistry

Cell death induced by the ER stressor thapsigargin involves death receptor 5, a non-autophagic function of MAP1LC3B, and distinct contributions from unfolded protein response components | Cell Communication and Signaling | Full Text
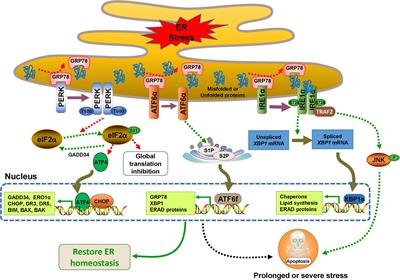
Frontiers | The Cross-Links of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, Autophagy, and Neurodegeneration in Parkinson's Disease

Endoplasmic reticulum stress signalling – from basic mechanisms to clinical applications - Almanza - 2019 - The FEBS Journal - Wiley Online Library

MANF Ablation Causes Prolonged Activation of the UPR without Neurodegeneration in the Mouse Midbrain Dopamine System | eNeuro

Transient Receptor Potential Ankyrin-1 and Vanilloid-3 Differentially Regulate Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Cytotoxicity in Human Lung Epithelial Cells After Pneumotoxic Wood Smoke Particle Exposure | Molecular Pharmacology

Molecules | Free Full-Text | Mipsagargin: The Beginning—Not the End—of Thapsigargin Prodrug-Based Cancer Therapeutics